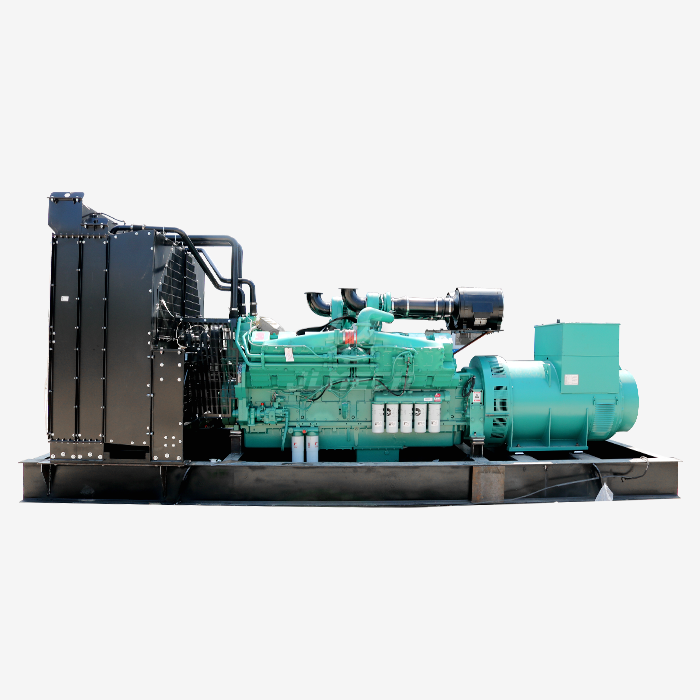
Auxiliary power systems for large generators encompass a range of components that support the main generator's operation. These systems manage essential functions such as starting the generator, cooling the engine, controlling fuel flow, and monitoring various parameters. For big diesel generators, which can range from hundreds of kilowatts to several megawatts in capacity, the auxiliary power requirements are proportionally significant and demand careful consideration in design and implementation.

What is an auxiliary power unit (APU) for diesel generators?
An auxiliary power unit (APU) for diesel generators is a secondary power source that supports the main generator's functions. It's essentially a smaller generator or battery system that provides the necessary power to start the main generator and run its ancillary systems when the primary engine is not operating. APUs are crucial for ensuring that large generators can start reliably, especially in emergency situations or in remote locations where immediate power availability is critical.
Key functions of APUs in large generator systems
APUs serve several vital functions in the operation of big diesel generators:
- Engine starting: Providing the initial surge of power needed to crank the main generator's engine.
- Battery charging: Maintaining the charge of the generator's main batteries.
- Powering control systems: Keeping critical electronic controls and monitoring systems operational.
- Climate control: Running heating or cooling systems to maintain optimal temperatures for generator components.
- Lighting and security: Powering essential lighting and security systems around the generator installation.
The size and capacity of an APU system depend on the specific requirements of the main generator. For instance, a 2000kW diesel generator might require an APU capable of delivering several kilowatts of continuous power to support its auxiliary systems effectively.
Battery vs. hydraulic starting systems for heavy-duty generators
When it comes to starting large generators, two primary systems are commonly used: battery starting systems and hydraulic starting systems. Each has its advantages and is suited to different applications and environments.
Battery starting systems
Battery starting systems are the most common method for initiating generator operation. They rely on high-capacity batteries to provide the necessary cranking power. For big diesel generators, these battery banks can be substantial, often consisting of multiple 12V or 24V batteries connected in series or parallel to achieve the required voltage and current capacity.
Advantages of battery starting systems include:
- Relatively simple and well-understood technology
- Lower initial cost compared to hydraulic systems
- Easier maintenance and replacement of components
- Suitable for most environmental conditions
However, battery systems can be vulnerable to extreme temperatures and may require more frequent maintenance to ensure reliability.
Hydraulic starting systems
Hydraulic starting systems use pressurized fluid to turn the generator's engine. These systems are often preferred in harsh environments or where extremely reliable starting is required, such as in offshore applications or in very cold climates.
Benefits of hydraulic starting systems include:
- Higher reliability in extreme conditions
- Longer service life with less frequent maintenance
- Ability to provide multiple start attempts without recharging
- Less affected by temperature extremes compared to batteries
The downside of hydraulic systems is their higher initial cost and the need for specialized maintenance skills.
Jlmech offers both battery and hydraulic starting options for our range of diesel generators, allowing customers to choose the system that best fits their operational needs and environmental conditions.
How much parasitic load do big diesel generator aux systems consume?
Parasitic load refers to the power consumed by the auxiliary systems of a generator when it's running. For big diesel generators, this parasitic load can be significant and needs to be accounted for when sizing the generator for a specific application.
Factors affecting parasitic load
The amount of parasitic load varies depending on several factors:
- Generator size: Larger generators typically have more auxiliary systems and thus higher parasitic loads.
- Environmental conditions: Extreme temperatures may increase the power needed for cooling or heating systems.
- Operational requirements: Generators with more sophisticated control and monitoring systems may consume more power.
- Efficiency of auxiliary components: Modern, high-efficiency components can help reduce parasitic load.
Typical parasitic load percentages
As a general rule, the parasitic load for large diesel generators can range from 3% to 10% of the generator's rated capacity. For example, a 1000kW generator might have a parasitic load of 30kW to 100kW. This power is used to run systems such as:
- Engine cooling fans and pumps
- Fuel transfer pumps
- Battery charging systems
- Control and monitoring electronics
- Auxiliary lighting and HVAC for generator enclosures
It's crucial to consider this parasitic load when specifying a generator for a particular application to ensure that the net power output meets the required demand.
Jlmech specializes in designing and manufacturing premium diesel generator sets that are trusted by global brands. Our big diesel generators are engineered for reliability in extreme conditions, featuring advanced soundproofing enclosures and vibration-dampening technology. They operate seamlessly in urban settings or rugged terrains, with AC outputs ranging from 20kW to 3000kW.
Our generators offer flexibility with rated AC voltages of 110V, 220V, or 380V, and frequencies of 50Hz or 60Hz. The engine speeds range from 1500 to 3000 RPM, catering to various operational requirements. Available in single or three-phase configurations, and in silent or open frame types, our generators are adaptable to diverse environments and applications.
Jlmech's commitment to quality is evident in our CE, Euro 5, EPA, and CARB certified products. We pride ourselves on our global expertise, with 3 R&D centers and 126 technical staff ensuring cutting-edge innovation. Our ISO9001-certified manufacturing process includes automated testing, guaranteeing the highest quality standards.
For industries requiring uninterrupted operations, Jlmech delivers robust, fuel-efficient power solutions. Our diesel generator sets combine high-performance engines with intelligent control systems, ensuring seamless power for factories, hospitals, data centers, and remote sites. We offer customization options including open type, silent type, trailer type, container type, and rainproof power station configurations to meet specific customer needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the auxiliary power system requirements for large generators is essential for ensuring reliable and efficient operation. From selecting the right starting system to accounting for parasitic loads, every aspect plays a crucial role in the overall performance of a big diesel generator.
For industries that demand uninterrupted power supply and robust performance, choosing the right generator and auxiliary systems is paramount. Jlmech, with its 29 years of experience in power solutions, offers a range of diesel generators designed to meet the most demanding requirements across various sectors.
Whether you're in the industrial manufacturing sector needing reliable backup power, or part of the healthcare industry requiring uninterrupted power supply for critical operations, Jlmech has the expertise and products to meet your needs. Our global presence, with 26 overseas offices, ensures that you receive rapid spare parts and technical support within 48 hours, no matter where you are.
Ready to explore how Jlmech's power solutions can benefit your operations? Contact us at skala@whjlmech.com to discuss your specific generator requirements and discover how our expertise can power your success.
References
- Johnson, R. (2022). Auxiliary Power Systems for Industrial Generators: A Comprehensive Guide. Power Engineering Journal, 45(3), 112-128.
- Smith, A. & Brown, T. (2021). Comparative Analysis of Battery and Hydraulic Starting Systems in Large Diesel Generators. International Journal of Power Systems, 18(2), 203-217.
- Garcia, M. et al. (2023). Parasitic Load Optimization in High-Capacity Diesel Generators. Energy Efficiency in Industrial Applications, 7(1), 45-62.
- Patel, K. (2020). Advancements in Auxiliary Power Units for Heavy-Duty Generators. Power Technology Review, 32(4), 78-95.
- Williams, E. & Taylor, S. (2022). Environmental Impact Assessment of Large-Scale Generator Auxiliary Systems. Sustainable Energy Solutions, 11(3), 301-318.
- Lee, H. (2021). Reliability Enhancement Strategies for Auxiliary Power Systems in Critical Infrastructure. Journal of Resilient Power Systems, 9(2), 157-173.