What power rating generator does my farm need?
Selecting the correct power generator for your agricultural operation is one of the most crucial decisions you'll make for ensuring operational continuity and productivity. Unlike residential applications, farms present unique power challenges with multiple high-starting-load motors, varying operational schedules, and critical systems that cannot afford downtime. Choosing the right farm generator requires careful calculation of your actual power needs rather than making assumptions. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps to accurately determine your farm's power requirements and select a generator that delivers reliable performance when you need it most.
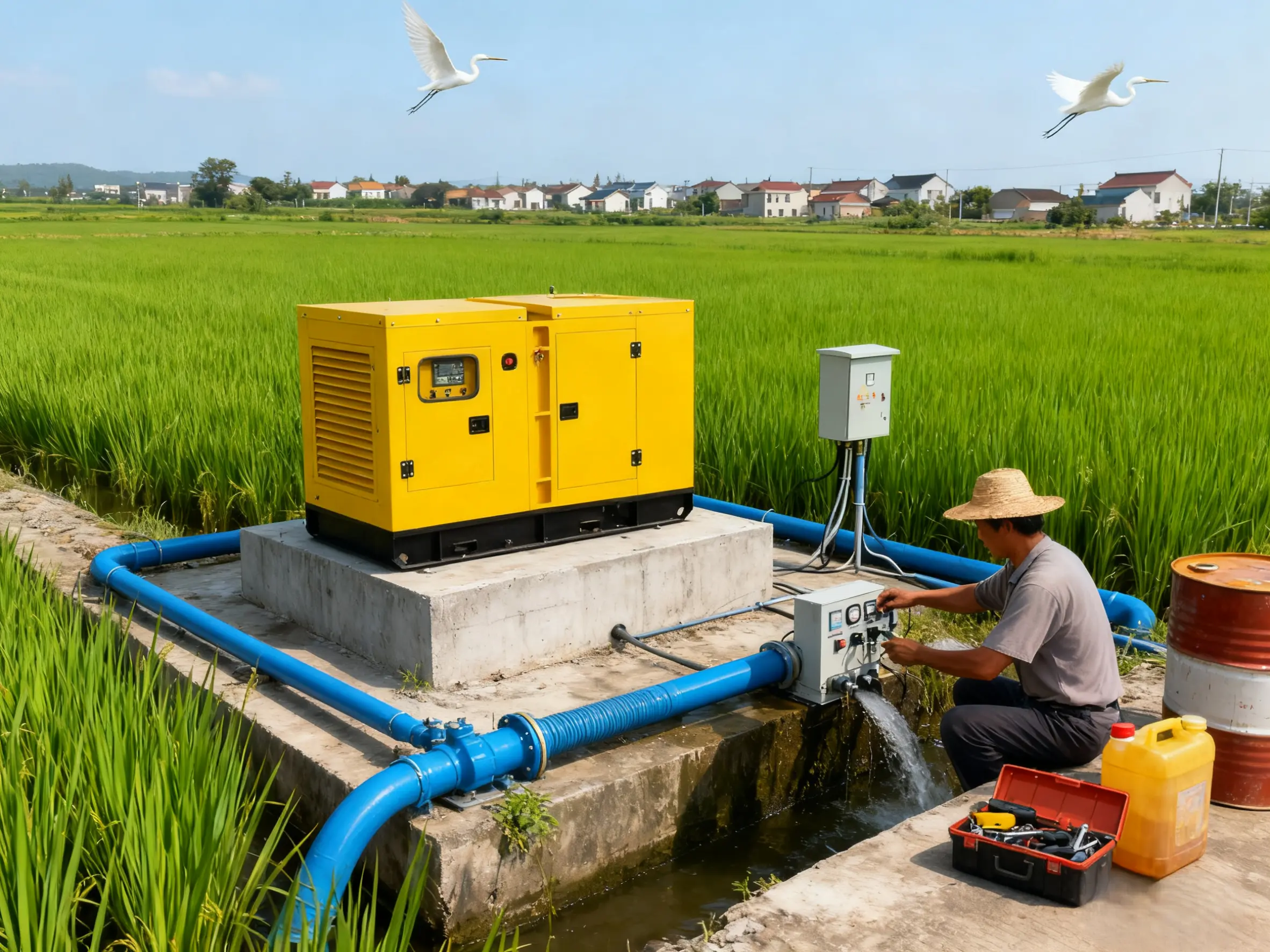

Assessing Your Power Requirements
The foundation of selecting the proper generator begins with a thorough assessment of all electrical equipment on your farm. Create a comprehensive inventory that includes every device that might require power during an outage.
Create a Detailed Equipment List:
Document all motors, equipment, and electrical devices
Include both essential and non-essential systems
Consider seasonal equipment that may be used intermittently
Identify Critical vs. Non-Critical Loads:
Critical: Refrigeration, ventilation systems, water pumps, basic lighting
Important: Milking machines, feeding systems, processing equipment
Non-critical: General barn lighting, workshop tools, convenience outlets
Understand Starting vs. Running Watts:
Electric motors require significantly more power to start than to run
Starting wattage can be 3-5 times higher than running wattage
Failure to account for startup surges will result in an undersized generator
This systematic approach ensures you capture all power requirements before moving to calculations.
Calculating Your Total Power Needs
Accurate power calculation requires understanding both running and starting wattages for all equipment. Follow this proven methodology to determine your farm's precise generator needs.
Collect Equipment Specifications:
Check nameplates on motors and equipment for wattage requirements
Document both running watts and starting (surge) watts
Note voltage requirements (120V, 240V, or 480V)
Calculate Total Running Watts:
Sum the running wattage of all equipment that may operate simultaneously
Group equipment by operational patterns (daily, seasonal, occasional)
Account for equipment that runs continuously versus intermittently
Account for Starting Surges:
Identify the single largest motor with the highest starting wattage
Add its starting watts to the running watts of all other equipment
This represents your peak power requirement
This calculation forms the basis for selecting a properly sized farm generator that can handle both continuous loads and temporary startup surges.
Farm-Specific Power Considerations
Agricultural operations have unique power characteristics that significantly impact generator selection and sizing decisions.
Motor-Dominated Loads:
Farms typically have numerous electric motors
Well pumps, ventilation fans, conveyor systems, and processing equipment
Each motor presents a significant startup surge challenge
Variable Operational Patterns:
Different seasons create different power demands
Consider both daily operations and seasonal peaks
Harvest seasons often demand maximum power availability
Multiple Operation Locations:
Power needs may be distributed across various barns and outbuildings
Consider centralized versus distributed generator solutions
Account for voltage drop over long distance power transmission
Understanding these agricultural-specific factors ensures your chosen farm generator matches your operational reality.
Generator Type Selection
Different farm operations benefit from different generator types and configurations. Consider these options based on your specific requirements.
Standby Generators:
Permanently installed with automatic transfer switches
Ideal for operations requiring immediate backup power
Higher initial investment but maximum convenience
Portable Generators:
More affordable initial purchase price
Suitable for smaller operations or specific equipment
Require manual setup and connection during outages
Limited power output compared to standby units
PTO Generators:
Powered by your tractor's power take-off system
Excellent value for farms with adequate tractor horsepower
Provide substantial power without a dedicated engine
Require tractor operation during power outages
Each farm generator type offers distinct advantages depending on your farm's size, budget, and operational requirements.
Installation and Safety Requirements
Proper installation is critical for generator safety, performance, and longevity. Follow these essential guidelines for optimal setup.
Location Considerations:
Install in well-ventilated areas away from combustible materials
Ensure adequate clearance for maintenance and airflow
Protect from weather elements while maintaining ventilation
Consider noise impact on livestock and neighboring properties
Electrical Connection Safety:
Always use a certified transfer switch
Never connect directly to building wiring without proper isolation
Use weatherproof connections and appropriate gauge wiring
Ensure proper grounding according to local electrical codes
Fuel System Requirements:
Maintain adequate fuel supply for expected outage durations
Implement proper fuel storage and handling procedures
Consider fuel stabilizers for extended storage periods
Plan for fuel delivery during extended power outages
These installation practices ensure your farm generator operates safely and reliably when needed most.
Maintenance and Operational Best Practices
Regular maintenance is essential for generator reliability. Implement these practices to ensure your generator is always ready for operation.
Scheduled Maintenance Tasks:
Regular oil and filter changes based on operating hours
Frequent inspection of air filters and cooling systems
Battery maintenance and testing for automatic start units
Exercise the generator regularly under appropriate load
Pre-Outage Preparation:
Keep fuel tanks filled during severe weather seasons
Test generator operation before anticipated need
Maintain an inventory of critical spare parts
Ensure all operators understand startup and shutdown procedures
Operational Monitoring:
Monitor power output and engine performance during operation
Watch for unusual noises, vibrations, or exhaust smoke
Keep detailed records of maintenance and operational hours
Schedule professional inspections annually
Proper maintenance ensures your agricultural power investment provides years of reliable service.
Cost Considerations and Budgeting
Understanding the total cost of ownership helps make informed decisions about your farm's power backup solution.
Initial Investment:
Generator purchase price varies by size and features
Installation costs including transfer switch and wiring
Permitting and inspection fees where required
Foundation and weather protection structures
Operating Costs:
Fuel consumption based on load and runtime
Regular maintenance parts and services
Potential professional service contracts
Replacement part inventory costs
Long-Term Value:
Consider generator lifespan and durability
Evaluate fuel efficiency across different load levels
Assess impact on farm productivity during outages
Factor in potential livestock and product losses without backup power
These financial considerations help determine the true value of your farm generator investment.
Conclusion
Our team specializes in helping agricultural operations select and implement the ideal power solutions for their specific needs. Contact us at skala@whjlmech.com to discuss your farm's generator requirements.
References
International Organization for Standardization. (2018). Reciprocating internal combustion engine driven generating sets — Part 1: Application, ratings and performance (ISO 8528-1:2018).
Generator Manufacturers Association. (2021). Guidelines for Rating and Application of Generator Sets. GMA Technical Publication TP-101.
National Fire Protection Association. (2020). Standard for Emergency and Standby Power Systems (NFPA 110).
Johnson, M. (2022). Emergency Power Systems: A Comprehensive Guide to High-Speed Diesel Generators. Power Engineering Quarterly, 45(3), 78-92.