Can a 3-phase generator be used for single-phase?
A common question we encounter in the power generation industry is whether a three-phase generator can be utilized for single-phase applications. The short answer is yes, but with important considerations. Understanding the fundamental difference between single phase and three phase generator systems is crucial before attempting such a configuration. While three-phase generators are engineered to deliver balanced power across three windings, various methods exist to adapt them for single-phase use. However, doing so incorrectly can lead to equipment damage, inefficient operation, and potential safety hazards. This comprehensive guide will explore the practicalities, limitations, and proper techniques for using a three-phase generator for single-phase loads.
Basic Generator Principles
To understand the compatibility between three-phase generators and single-phase loads, we must first examine how each system produces and delivers power.
Single-Phase Generators: These units produce a single alternating current (AC) waveform through one set of windings. They typically have two output terminals and are commonly used in residential applications for lighting and small appliances, providing voltage levels like 120V or 240V .
Three-Phase Generators: These systems generate three separate AC waveforms, each spaced 120 degrees apart . This design creates a more consistent power delivery compared to the pulsating nature of single-phase power . They contain three sets of windings arranged in either a Delta (Δ) or Star (Y) configuration and excel at powering industrial machinery and large motors .
The key difference between single phase and three phase generator systems lies in this fundamental architecture: single-phase uses one set of windings while three-phase employs three sets with precise phase separation .
Key Differences Between Single-Phase and Three-Phase Generators
Understanding the practical implications of these different designs helps explain why proper adaptation is necessary when using three-phase generators for single-phase applications.
Power Delivery Consistency: Single-phase power delivery is pulsating, while three-phase systems provide constant power . This gives three-phase systems a significant advantage in running industrial equipment smoothly.
Efficiency and Capacity: Three-phase generators are more efficient for the same physical size . They can deliver up to 150% more power than similarly sized single-phase units , making them ideal for heavy industrial applications.
Voltage Options: Three-phase systems offer multiple voltage configurations. In North America, common configurations include 120/208V wye and 277/480V wye, while single-phase typically offers 120/240V .
Application Scope: Single-phase generators suffice for most residential and light commercial needs, while three-phase generators power industrial facilities, large commercial buildings, and manufacturing plants with heavy machinery .
Conductor Requirements: For the same power delivery with equal power loss, a single-phase system may require approximately 33% more conducting material compared to a three-phase system .
These distinctions highlight why understanding the difference between single phase and three phase generator systems is essential for proper application and adaptation.
Using 3-Phase Generators for Single-Phase Loads
While possible, using a three-phase generator for single-phase loads requires careful consideration of several technical factors to prevent equipment damage and ensure safe operation.
The Imbalance Problem: When you connect a significant single-phase load to just one winding of a three-phase generator, it creates an unbalanced system . This imbalance can cause:
Overheating in the heavily loaded winding
Voltage fluctuations and instability
Reduced efficiency and potential damage to the generator
Manufacturer Guidelines: Always consult your generator's manual first. Some modern three-phase generators are specifically designed to handle limited single-phase loading, while others explicitly prohibit it.
Power Derating: When using a three-phase generator for single-phase applications, you must typically derate the unit (use it at less than its rated capacity). As a general rule, the single-phase output should not exceed 1/3 of the generator's three-phase rating to prevent imbalance issues.
Connection Methods: The proper connection method depends on your generator's winding configuration (Delta or Wye) and the specific single-phase voltage requirements.
Methods for Conversion
Several technical approaches exist for safely adapting three-phase generators to single-phase loads, each with varying complexity and effectiveness.
Phase Conversion Equipment: The most reliable method involves using a phase converter, which transforms single-phase power to three-phase or manages the load distribution from a three-phase source. There are different types available, including:
Static Phase Converters: Simple but limited, these provide starting capability for three-phase motors from single-phase power but don't create true three-phase operation.
Rotary Phase Converters: These use an induction motor to generate true three-phase power from single-phase input, offering better performance for running three-phase equipment.
Electronic Converters: Modern solid-state converters use electronic components to create balanced three-phase power . These systems often provide better voltage regulation and can handle varying loads more effectively.
Specialized Winding Techniques: Research has shown that with specific capacitor configurations and winding connections, three-phase induction generators can be adapted for single-phase operation while maintaining relatively balanced voltages . One approach uses "two capacitors connected to two different single-phase voltage sources" to create proper phase balancing .
Electronic Capacitor Systems: Recent developments include using electronic capacitors and converter systems to enable three-phase induction generators to operate with single-phase grids while maintaining performance .

Professional Applications
In industrial and commercial settings, specialized equipment makes the conversion between single-phase and three-phase power more seamless and efficient.
Converter Systems: Industries increasingly use advanced converter systems based on power electronic devices like IGBTs . These systems can include front-end converters that offer bidirectional power flow and machine-end converters that handle generator excitation .
Balancing Transformers: Some systems employ balance transformers with PWM rectifier control strategies to convert single-phase to three-phase power while maintaining high power factors and suppressing harmonic currents .
Grid-Connected Solutions: For renewable energy applications like wind power, researchers have developed systems where "three-phase induction generators can operate as grid-connected single-phase generators using electronic capacitors" .
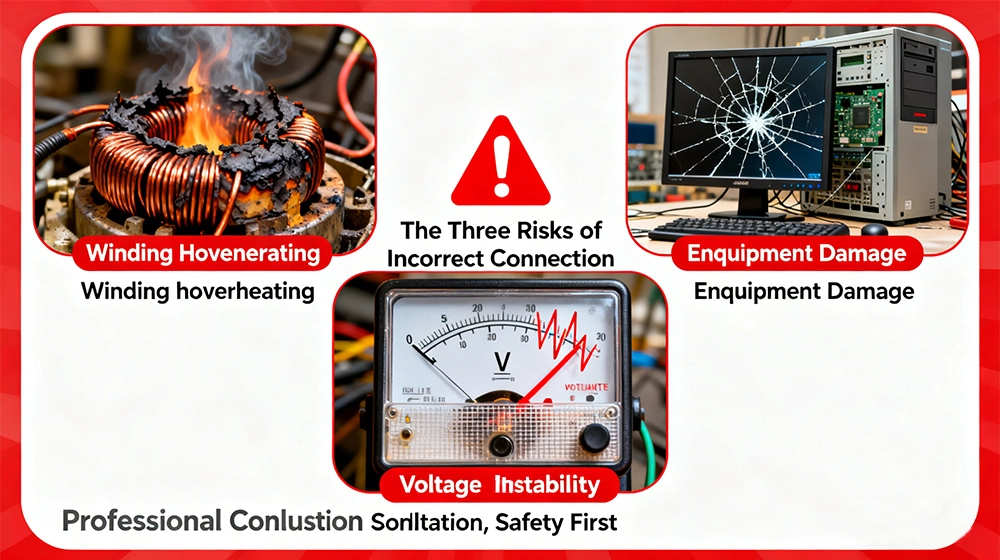
Limitations and Risks
Attempting to use a three-phase generator for single-phase applications without proper equipment and expertise poses several significant risks.
Generator Damage: Severe phase imbalance can cause overheating in the overloaded winding, potentially destroying insulation and leading to costly generator repairs or replacement.
Reduced Efficiency: Operating a three-phase generator with unbalanced loads typically results in lower overall efficiency, increased fuel consumption, and higher operating costs.
Voltage Instability: Connected equipment may experience voltage fluctuations that can damage sensitive electronics or cause operational issues with motors.
Voided Warranties: Many generator manufacturers will void warranties if their three-phase units are used for significant single-phase loading without proper phase conversion equipment.
Safety Hazards: Improper connections can create shock hazards, fire risks, and other dangerous conditions.
Practical Recommendations
For those considering using a three-phase generator for single-phase applications, these practical guidelines can help ensure safe and effective operation.
Consult Professionals: Always engage with qualified electrical engineers or generator specialists before attempting to connect single-phase loads to a three-phase generator.
Use Proper Conversion Equipment: Invest in appropriate phase converters or transformers rather than attempting direct connections that create imbalance.
Follow Manufacturer Specifications: Adhere strictly to the generator manufacturer's guidelines regarding single-phase loading limitations.
Consider Future Needs: If you anticipate needing both single-phase and three-phase power regularly, consider purchasing a generator specifically designed for both applications.
Implement Load Monitoring: Install monitoring equipment to track load balance across phases and prevent dangerous imbalance conditions.
Regular Maintenance: When operating under adapted conditions, increase the frequency of generator maintenance and inspection to identify potential issues early.
Conclusion
While it is technically possible to use a three-phase generator for single-phase applications, doing so requires careful planning, proper equipment, and thorough understanding of the significant difference between single phase and three phase generator systems. The most reliable approach involves using appropriate phase conversion equipment rather than directly connecting single-phase loads to one phase of a three-phase generator. Understanding these principles ensures safe operation, protects your equipment investment, and delivers reliable power when you need it most.
Our technical team can help you select the right generator configuration for your specific single-phase and three-phase power requirements. For professional guidance and generator solutions, please contact us at skala@whjlmech.com.
References
IEEE Power & Energy Society. (2017). IEEE Recommended Practice for Emergency and Standby Power Systems for Industrial and Commercial Applications. IEEE Std 446-2017.
International Organization for Standardization. (2018). Reciprocating internal combustion engine driven generating sets — Part 1: Application, ratings and performance (ISO 8528-1:2018).
Generator Manufacturers Association. (2021). Guidelines for Rating and Application of Generator Sets. GMA Technical Publication TP-101.
National Fire Protection Association. (2020). Standard for Emergency and Standby Power Systems (NFPA 110).











